Should You Invest in a Home Charger or Stick with Public Networks?
Navigating Electric Vehicle Charging Choices for Businesses and Consumers
Owning an electric vehicle raises a vital question for individuals businesses and engineers alike: should one install a home charger or rely on public charging infrastructure. This discussion explores key factors that guide that choice in a clear knowledgeable manner.
Understanding the Charging Landscape
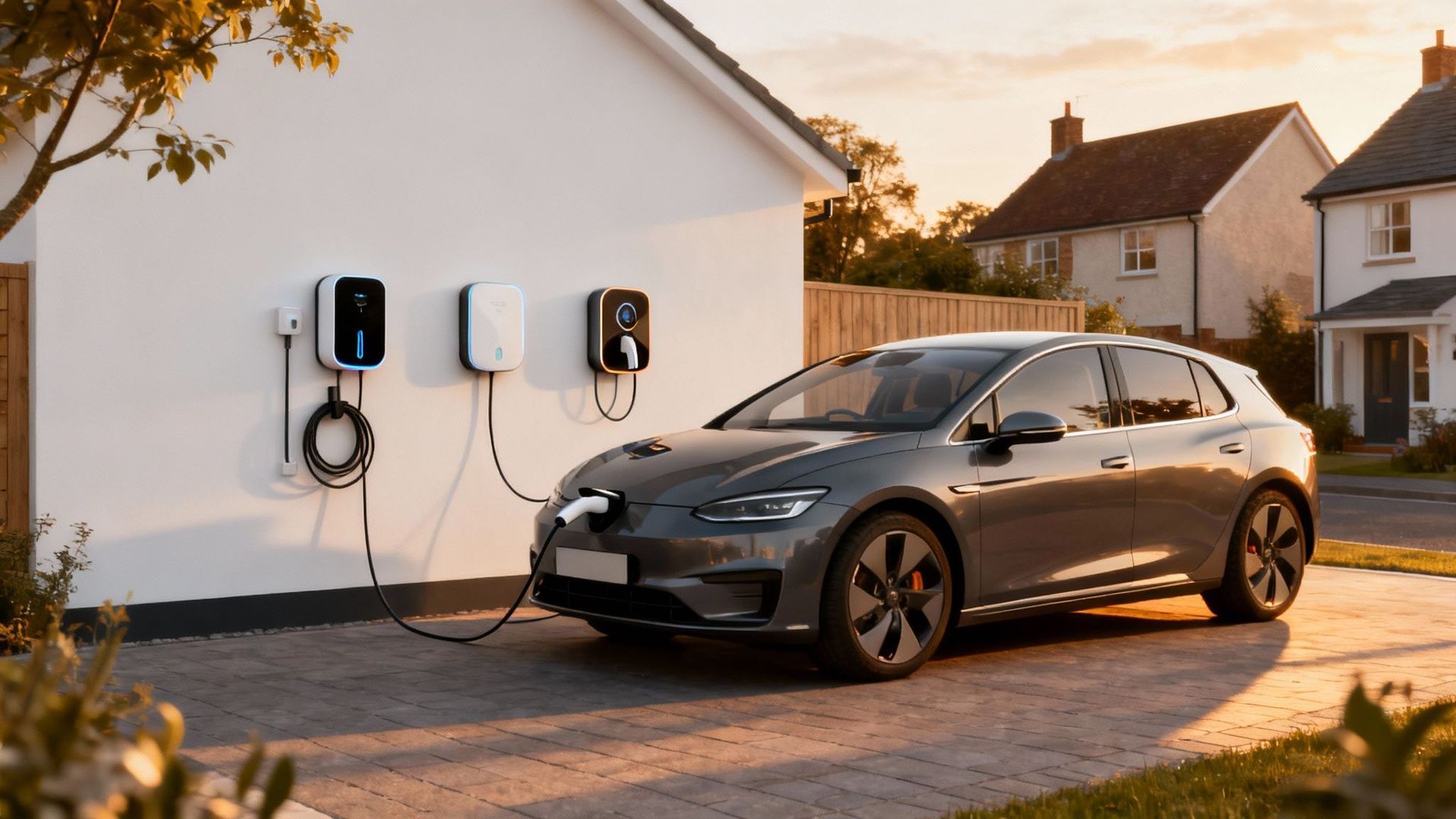
Electric vehicle charging falls into two broad categories: home charging and public network charging. Home charging typically involves installing a dedicated unit at a residence or business premises for personal or fleet use. Public network charging includes workplace chargers motorway service station points or urban charging hubs accessible to many users.
Cost Comparison
One of the most critical considerations in deciding between home charging and public networks involves long term cost implications.
- Installation and upkeep of a home charger can involve an initial outlay yet often results in lower per kilowatt hour rates especially during off peak periods.
- Public chargers may impose variable pricing dynamic tariffs or per minute usage fees.
- Maintenance of a home unit stays within control of the owner while public networks handle their own upkeep though costs may be reflected in higher usage fees.
Convenience and Accessibility
Convenience plays a major role in charging strategy.
- Home charging enables charging overnight while the vehicle is idle ensuring a full battery every morning.
- Public networks pose variables such as queuing availability waiting times or detours during a busy commute or trip.
- For businesses with fleet vehicles home or depot chargers provide dedicated access whereas public charging may suit occasional top ups.
Speed and Reliability
Understanding charging speed and reliability helps shape the decision.
- Home chargers often deliver reliable performance during predictable times albeit at moderate speeds depending on the home electrical supply.
- Public fast or ultra rapid chargers can offer significantly faster charging though their availability may fluctuate and downtime or maintenance could occur.
- Reliability of public networks varies by provider location and infrastructure maturity especially during peak periods or in rural areas.
Strategic Use Cases
Different users gain from tailored approaches.
- Business owners managing fleets or EV promotions may benefit from home or depot chargers that offer cost predictability and scheduling flexibility.
- Consumers seeking daily convenient charging will enjoy the simplicity of overnight home charging unless their property cannot support installation.
- Engineers and technical users might integrate smart charging to optimise energy use either at home or through networked systems.
- Marketers concerned with branding associated with EV sustainability may highlight home charging as a customer benefit or combine it with public network partnerships.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages of Home Charging
• Convenience of overnight charging
• Predictable energy costs
• Control over installation and maintenance
• Flexibility with smart scheduling if enabled
Limitations of Home Charging
• Upfront installation cost
• Possible upgrades needed to electrical supply
• Limited mobility charging only available at one location
Advantages of Public Networks
• Access during travel or away from home
• Fast charging options in many areas
• No installation required
Limitations of Public Networks
• Potentially higher rates
• Waiting time or availability challenges
• Reliability depends on provider and location
Enhancing Your Decision with Smart Integration
Smart charging technologies can augment both home and public charging experiences.
Integrating time aware charging can reduce energy cost by taking advantage of off peak rates.
Remote monitoring enables users to check charging status whether at home or using a public network.
For businesses centralised platforms can track usage across home and public sites improving visibility and cost management.
Tailoring the Approach to Your Needs
Consider these guiding questions:
- How often do you commute or travel beyond your home range?
- Can your premises support installation of a suitably powerful charger?
- Are cost savings a priority or is flexibility more important?
- Do you or your business require fast turnaround charging or is overnight replenishment sufficient?
- Can you integrate smart systems to manage energy load and report usage efficiently?
Conclusion
Deciding whether to invest in a home charger or rely on public networks depends on individual or organisational needs. Home charging excels at convenience predictability and control while public networks offer flexibility especially on longer journeys or when away from base. Businesses engineers and savvy consumers can benefit from a combined approach using home installation alongside occasional use of public infrastructure especially when enhanced by smart charging systems.
By aligning your charging infrastructure strategy with your usage patterns access requirements and energy management goals a well informed choice will strengthen your EV experience and support long term sustainability of your transport or organisational operations.